
Newsletter Subscribe
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter

Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
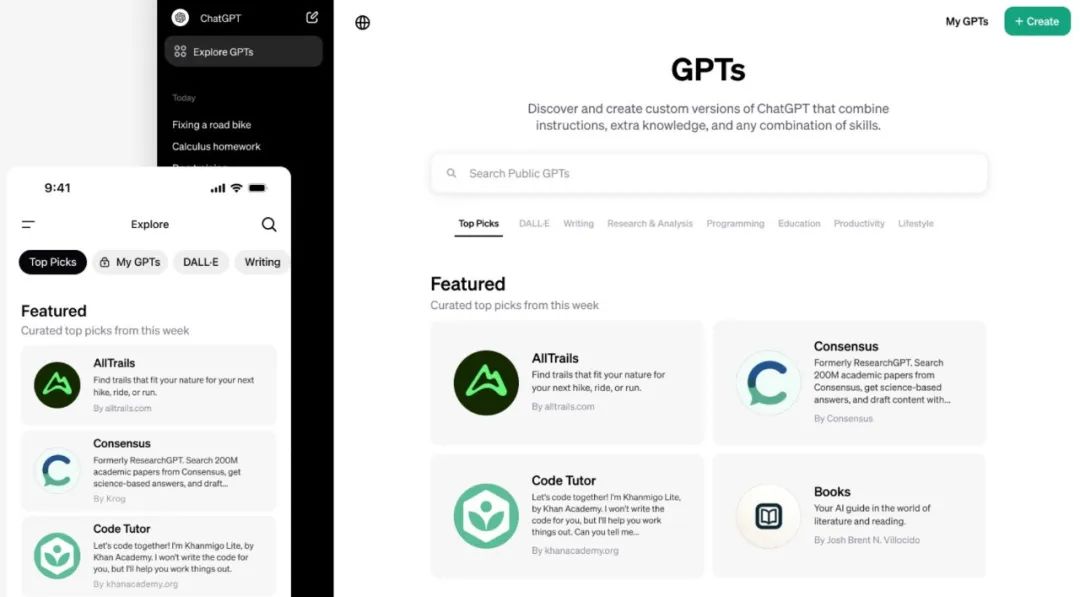
The much-anticipated GPT Store by OpenAI is finally live!
Since the introduction of Custom GPTs at the OpenAI Developer Conference in November last year, a staggering 3 million GPTs have been created in just two months.

On January 11, 2024, OpenAI officially launched the GPT Store for paying users of ChatGPT Plus, Team edition, and Enterprise edition.
The Team edition, a new paid version priced between Plus and Enterprise editions, costs $30 per person per month or an equivalent of $25 per person per month for annual billing. Team edition offers a higher GPT-4 usage limit than Plus and allows teams to share and manage created GPTs. It includes an admin console for workspace management, supporting up to 149 users.
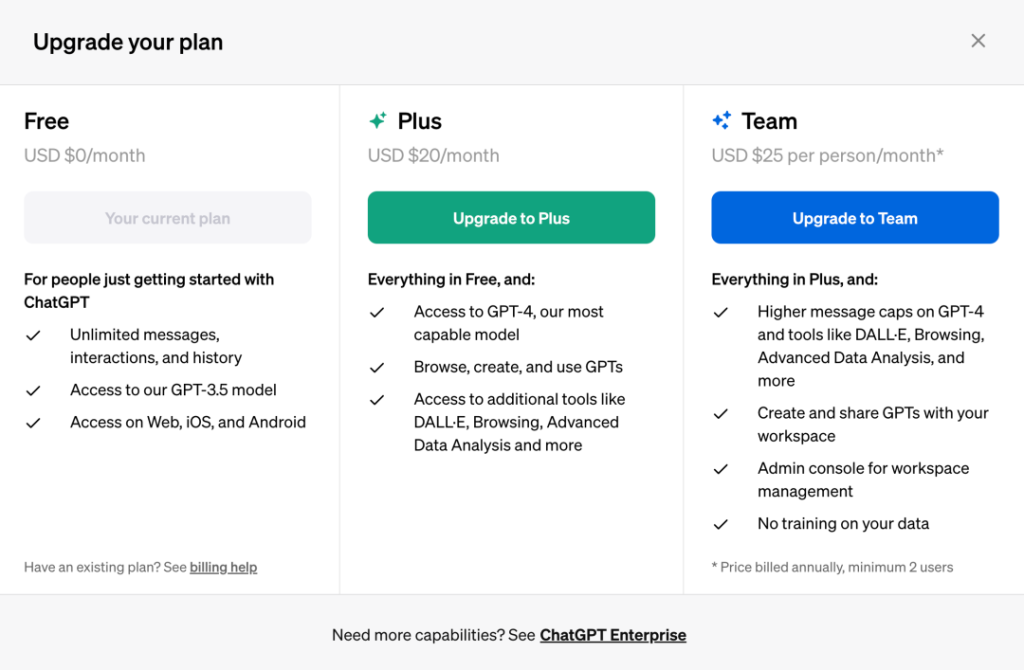
According to OpenAI, the GPT Store aims to establish and nurture a community of developers, researchers, and AI enthusiasts, showcasing the best and most creative uses of GPT.
As of now, the GPT Store is consistent with the previously revealed features, including search, categorization, top picks, and trending.
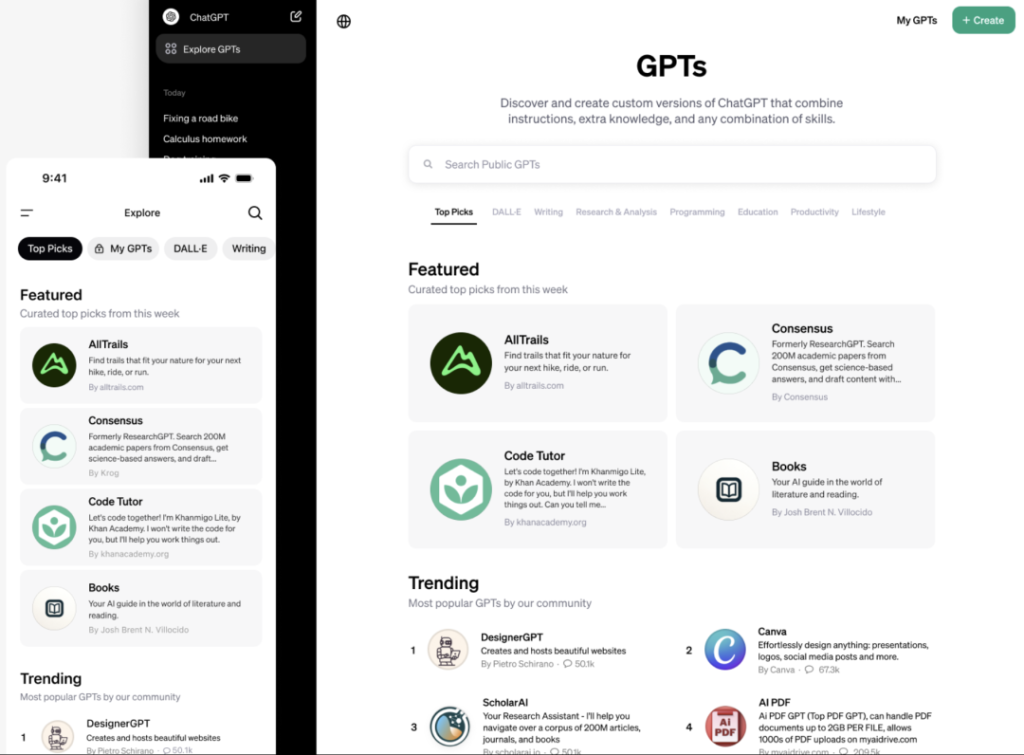
Regarding the burning question of “income,” OpenAI has stated that the GPT creator income program will be launched in the first quarter of this year. While GPT creators currently cannot profit directly, the initial batch of U.S. “Builders” can earn rewards based on “user engagement with their GPTs.” More details on how to monetize GPTs will be disclosed later.
Reflecting on the launch of the App Store by Apple in 2008, which not only provided an efficient distribution platform for third-party software but also yielded substantial profits for Apple, the GPT Store can be perceived as the “App Store” of the AI realm, with profound significance and impact. It not only revolutionizes traditional AI application development and distribution models but also offers users a richer and more personalized AI application experience.
This marks a “no-code revolution,” allowing users to create personalized GPTs with minimal programming knowledge, positioning the GPT Store as an excellent opportunity for ordinary individuals to earn their first AI income.
Moreover, GPT applications created by users will not only be hosted and developed in the GPT Store but will also receive official recommendations and user experience evaluations, fostering continuous optimization and innovation by developers to meet market demands. This lays a crucial foundation for building a healthy, sustainable technological ecosystem.
The GPT Store is likely being rolled out gradually, with U.S. users already able to see the new “Explore GPTs” page.
The page has a new “Global View” switch in the top left corner, presumably allowing users to search and view GPTs from different regions once fully launched.
Currently, the displayed GPT categories include Featured Picks, DALL·E, Writing, Productivity, Research & Analysis, Programming, Education, and Lifestyle.
OpenAI’s official introduction mentions that these GPTs are contributed by both partner developers and community creators, with a weekly update to the “Featured Picks” category showcasing influential GPTs. The initial six GPTs selected by OpenAI mainly come from partner contributions, featuring:
Among these, Consensus is currently the most popular GPT within the community. The top 12 trending GPTs are all practical tools, including AI assistants for handling PDF documents, scientific research, image and video generation, and more.
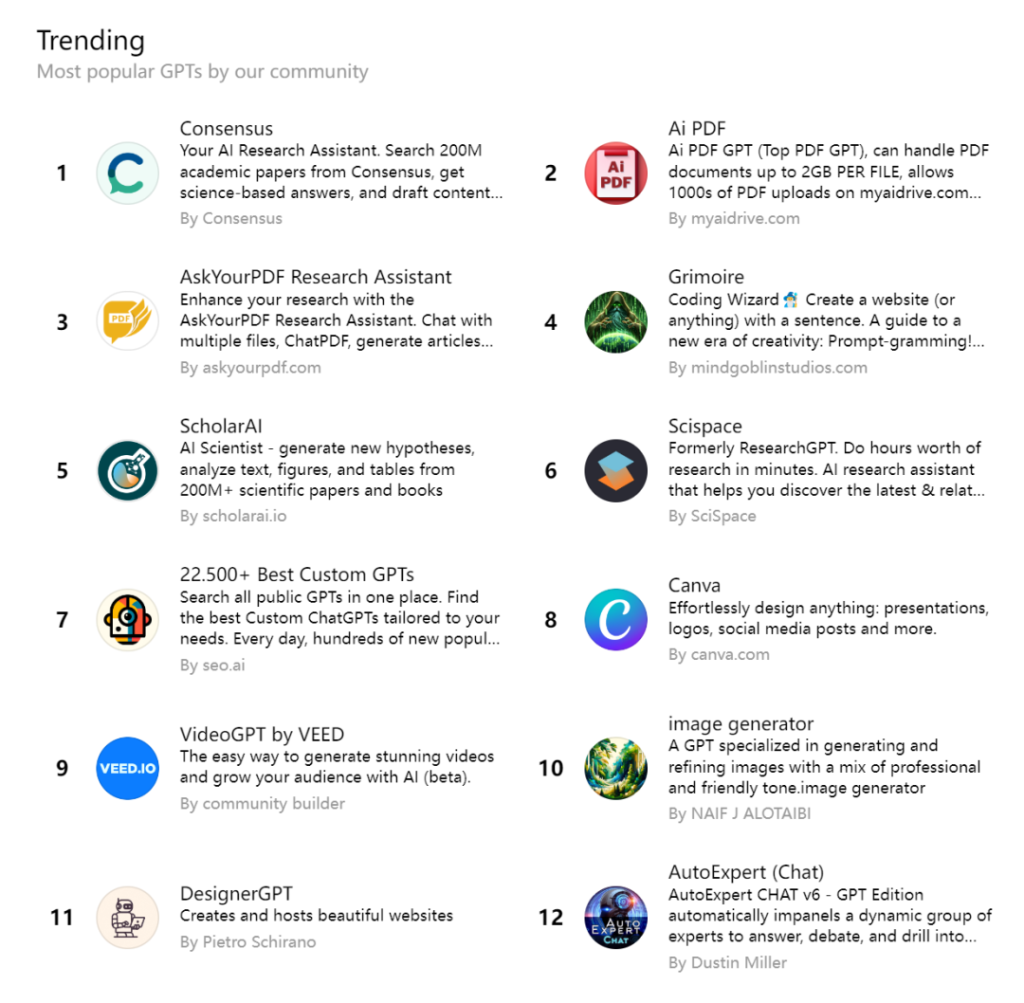
No wonder Sam Altman jokes that while the GPT Store has many useful GPTs, it seems like “everything is waifus” GPTs have disappeared.

So, how are “trending” GPTs ranked? How does OpenAI choose GPTs to feature?
According to the official documentation, OpenAI actively reviews user interactions with GPTs and performs trend analysis for different GPT categories.
The key factors for becoming a “Featured” GPT include:
The ChatGPT team seeks GPTs that contribute to meaningful user experiences, innovation, and ethical considerations within the community. This includes different types of GPTs, and consideration of current events and seasonal activities to showcase relevant GPTs.
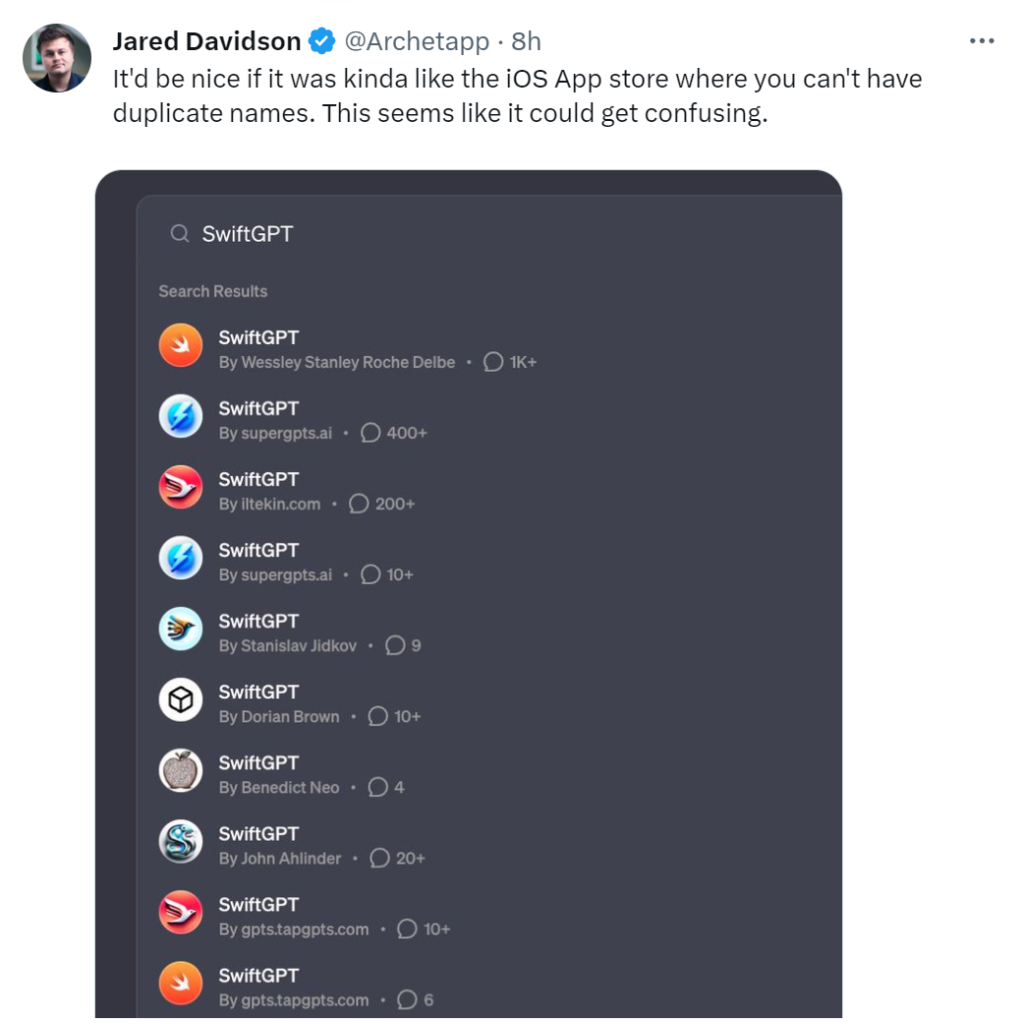
In addition to rankings, entering keywords into the search box reveals more related GPTs. Notably, search results are arranged in descending order based on statistics, such as Consensus having over 300,000 interactions.
Unlike the iOS store, the GPT Store currently does not enforce the prohibition of duplicate names, allowing for a plethora of GPTs with the same name.
All users subscribed to ChatGPT Plus can create GPTs and share them with others. So, how can beginners quickly create a GPT and launch it on the store?
Firstly, access the GPT creation page, with the left side for creating the GPT and the right side for previewing its effects.
On the “Create” page for GPTs, users can send messages to the GPT builder to quickly complete the GPT’s construction through interaction with the AI assistant, supporting Chinese language dialogue.
For example, to create an “AI News Assistant,” after expressing your needs, the GPT builder will prompt questions to guide you on naming, topics of interest, what to avoid, interactive methods, and more.
Once created, users can test the GPT’s capabilities in the preview and make adjustments.
After confirmation, it’s time to prepare for the GPT’s release. On the “Configure” page, users can see that the GPT builder has already filled in most of the information, which can be further adjusted. For advanced users, manual naming and setting of the GPT’s description are available, including options such as:
When saving and publishing the GPT, users can choose the category and public scope. For store listing, select “Accessible to everyone.”
Before listing in the store, the Builder configuration file must be verified (Settings → Builder Configuration → Enable Name or Verified Website).
Upon successful release, users can immediately access the GPT. All Plus users can converse with it, while free users can search and view it but cannot engage in dialogue. Creators can change the GPT’s sharing settings and remove it from the store at any time.
For issues encountered during use, such as generating illegal content, users can report to OpenAI. It is emphasized that, in addition to existing safety measures in the product, the team has established a new review system, including manual review, automatic review, and user reports. GPT creators should consult the usage policy and GPT brand guidelines to ensure compliance.
According to the latest usage policy, GPTs like AI lovers are not allowed to be listed on the GPT Store.